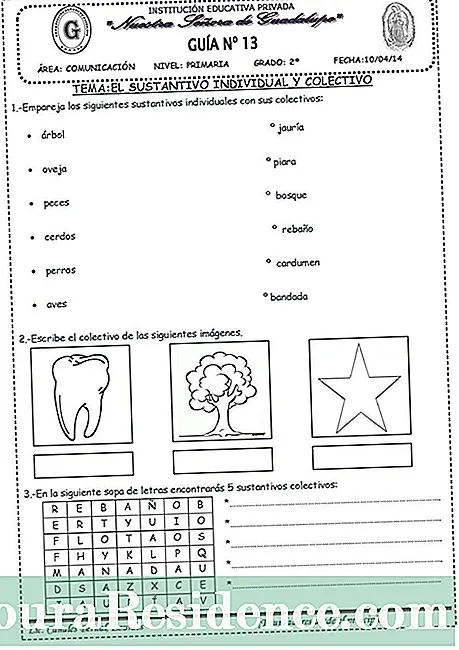
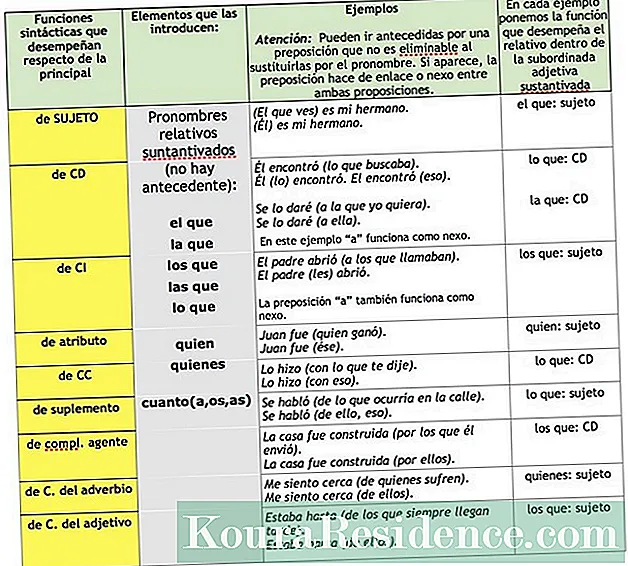
Content
The ductile materials They are those capable of plastic and sustainable deformation, without breaking or violating its structure, in the face of the sustained action of a force. In fact, a characteristic of them is that through a sustained longitudinal tension fibers or threads of smaller size but the same nature are obtained.
Ductile materials are precisely the opposite of brittle materials. But they should not be confused with malleable materials.
This does not mean that ductile materials cannot break; in fact, they do, but after having suffered notorious deformations. Nor does it mean that ductile materials are soft; the force necessary for its deformation is considerable, and in the event of weak forces so will its change of shape, usually elastic and reversible.
The deformation of ductile materialsFurthermore, it can be increased in the presence of hot, without reaching the margins of molten, and is indirectly measured by resilience, especially in metals. The latter are the most common ductile materials, since their atoms They are configured in such a way that they can slide over each other, thus allowing the production of wires and threads of different thicknesses.
Ductile materials are valued in the metallurgical and tool-making industryas they can take specific shapes before breaking. However, insistent and repeated deformation will lead to fatigue metal and its breakage, further evidenced by the increase in temperature in the area on which the deforming force affects.
Examples of ductile materials
- The iron. Also called iron and represented by the chemical symbol Fe, it is the fourth most abundant element in the earth's crust, and the most abundant in planetary mass because the planet's core is made up of iron and nickel in liquid state, which when moving generate a powerful magnetic field. It is a malleable, gray metal with magnetic properties and extreme hardness and density. Therefore, in its pure state, the latter prevents it from being useful, so it is alloyed with carbon to obtain the family of steels, which according to the proportion of this element present may be more or less ductile and more or less less resistant.
- Timber. It is a fairly ductile organic material, depending on its nature and the percentage of moisture present in it, as well as the location of the nodes it contains. However, being fibrous, it can easily open under forces perpendicular to its grain.
- The steel. This name is called a mixture of iron and carbon (up to 2.14%) which yields a hard and relatively ductile material, especially combined with boron to form wires of superficial hardness and very high ductility, or in corrugated steel used in the construction sector. This makes it ideal to resist weights without fracturing the concrete, but allowing minimal deformations according to the weight dimension.
- Zinc. Zinc (Zn), an essential element for life, in its pure state it has high ductility and malleability, so it is possible to roll it into sheets, tension and deform it, but the presence of minimal contaminants from other elements is enough to make it brittle and fragile. It is essential in alloys such as that produced by brass.
- The Lead. This metallic element of the periodic table, with the symbol Pb, was not recognized at the time as metallic due to its enormous molecular elasticity. It is a heavy, grayish, flexible and easily meltable metal. It is used today as a cable cover, since its unique ductility makes it highly appropriate, as it can be stretched to suit the needs to be covered.
- Brass. Copper (70%) and zinc (30%) alloy, characterized by its very high ductility that makes it an ideal material for the manufacture of containers and containers, as well as tools that do not require extreme hardness. Combined with tin it makes it resistant to oxide and saltpeter, in addition to being very malleable.
- Plasticine. Extremely ductile, this plastic substance composed of calcium, petroleum jelly and aliphatic compounds, was invented in 1880. Usually made of colors and associated with the world of children's learning, it is characterized by its ability to be deformed without breaking, allowing its simple work with the hands. , instruments or any type of surface.
- Copper. Copper (Cu) is a bright reddish transition metal, which together with gold and silver are the better drivers metallic electricity.For this reason, it is the preferred metal when building electrical cables and both electrical and electronic components, since it is also economical, malleable and ductile.
- Platinum. This heavy, malleable and ductile grayish-white transition metal is valued in jewelry and laboratories as being corrosion resistant and precious in nature. It is also common to find platinum (Pt) in catalytic additives for automobiles, electrical contacts and other types of applications that take advantage of its resistance.
- The aluminum. Aluminum (Al) is a non-ferromagnetic metallic element and the third most common in the earth's crust. It is highly used in the industry of the materials, although it can be extracted as a metal only from bauxite, due to its properties such as low density, high conduction of heat and electricity, high resistance to corrosion, economical cost and alloability. For this reason it has been the most used metal, along with steel, in the 20th century. Although its natural ductility does not seem to be extreme, in foundry alloys this character is reinforced, as well as its resistance to stress and corrosion, usually through the incorporation of Silicon (5 to 12%) and magnesium.
They can serve you
- Examples of Natural and Artificial Materials
- Examples of Elastic Materials
- Examples of Recyclable Materials
- Examples of Insulating Materials
- Examples of Semiconductor Materials
- Examples of Superconducting Materials