Author:
Peter Berry
Date Of Creation:
14 February 2021
Update Date:
12 May 2024
Content
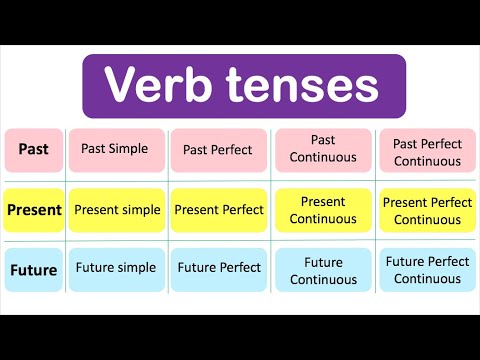
- Classification of verb tenses
- Examples of sentences with indicative tenses
- Examples of sentences with subjunctive tenses
The verbal tense It is the grammatical category that locates the performance of an action or locates a state. An action can be placed in the present tense (love, fear, part); past time (loved, feared, departed) or future tense (will love, fear, depart).
The verb tense is marked by the elements that correspond to the forms of the conjugation. They are called simple if the action is expressed with a single word (we love). The compounds are expressed with more than one word, generally an auxiliary verb and a participle (we have loved).
- See also: Types of verbs
Classification of verb tenses
Indicative mode times
- Present (I love, I fear, I give birth). Place the action at the time it is expressed or in the immediate future. It expresses permanent or stable situations. Describe repeating actions or routines. For example: I go to English on Mondays and Thursdays.
- Simple past perfect (loved, feared, departed). It expresses actions that began and ended in the past, that occurred in a timely manner, or that interrupted other past actions. For example: Last year studied contemporary history in school.
- Imperfect past (loved, feared, departed). It expresses actions of the past whose beginning and end are not specified. They also convey the regularity or continuity of an action in the past. For example: Roman traveled inside every month.
- Past perfect compound (I have loved, I have feared, I have departed). It expresses actions that have already ended but that continue to have an impact in the present. For example: Last week I have transplanted the pines to these pots.
- Past perfect (he had loved, he had feared, he had parted). This time is almost in disuse in the Castilian language. It conveys an event that is prior to another past event and that has occurred soon after. For example: Barely had received his exam grade, Juan went to celebrate with his classmates.
- Past perfect (I had loved, I had feared, I had departed). It conveys that a past action was prior to another that also occurred in the past. For example: When I went to talk to Tomás, I already know had found out of what happened.
- Composite future (will have loved, will have feared, will have departed). It expresses that something will happen in relation to the moment in which it is pronounced but, at the same time, it is a previous action with respect to another to come. For example: When my parents return from Europe I will I will have finished the completed.
- Simple future (will love, fear, depart). It expresses an action that is about to take place, absolutely. For example: My friend will come to study this afternoon.
- See also: Indicative mode
Tenses of the subjunctive mood
- Present (love theme part). It is often used as an imperative or in subordinate clauses, along with certain expressions that express a present or future action. It is a hopeful future. For example: I would love that you approve that exam.
- Perfect tense (I have loved, I have feared, I have departed). It is a compound tense, similar to the present subjunctive. Express admiration or actions that are over but are related to the action in the topic sentence. For example: Once you finished homework, I'll take you out for ice cream.
- Imperfect past (love / love, fear / fear, part / part). It is used in subordinate clauses, after certain formulas. It can refer to something that happened simultaneously or before the moment it is expressed, depending on whether the main verb of the sentence is in the past or present. For example: I would really appreciate it if you helps to carry these suitcases.
- Past perfect (would / would have loved, would / would have feared, would / would have parted). It is composed of the past imperfect of the subjunctive of the verb to have and the participle of the verb in question. It transmits actions that could have occurred or would have occurred in the past, if the circumstances had been different. For example: If you I would have said Before I was promoted, I'm sure it wouldn't have helped me.
- Perfect future (would have loved, would have feared, would have parted). It is composed of the auxiliary to have in future imperfect and by the passive participle of the verb in question. This time contains an idea that is past. For example: One who would have studied expressionism, you will enjoy the exhibition in the museum.
- Imperfect future (I will love, sing, partiere). It is in disuse, except in the legal field. It is similar to the past imperfect or the present subjunctive. For example: Everyone who I will obey to the rules, you will not have problems.
- See also: Subjunctive mood
Examples of sentences with indicative tenses
- Am quiet for tomorrow's exam. [Present]
- The last time I went to the Capital Visited to all my relatives. [Simple past perfect]
- When I have finished homework, I went to the park. [Past perfect]
- My students know they have prepared for weeks for this exam. [Preterite perfect compound]
- I've done a lot of exercise during the holidays. [Preterite perfect compound]
- Dew prepared waffles the last time we met. [Simple past perfect]
- Walked to work every day. [Imperfect Past]
- Barely there was sunset, we started playing the guitar. [Past perfect]
- Stephen there was alreadybought the passage when we organize the trip. [Past perfect]
- Raul worked in a factory when he was single. [Imperfect Past]
- Study French twice a week. [Present]
- Diana took out to walk his dog to that square, until he moved. [Imperfect Past]
- We had already arrived to the hotel when my aunt called. [Past perfect]
- By the time the baby is born, I already will have decorated your room. [Future compound]
- ¿You want a coffee? [Present]
- Enrique He has traveled to Peru several times. [Perfect tense]
- In the last year of the course, they arrived many exchange students. [Simple past perfect]
- There will be desserts for all tastes. [Simple future]
- Loved get out of school and hang out with my neighborhood friends. [Imperfect Past]
- It was a huge surprise your visit. [Simple past perfect]
- Already I will have started to work when I finish the thesis. [Perfect future]
- You we will provide assistance to anyone who requests it. [Simple future]
- My granny cooked a cake every time we went to visit her. [Imperfect Past]
- He had than quit your job after that incident. [Simple past perfect]
- Barely had known the news, he began to cry. [Past perfect]
Examples of sentences with subjunctive tenses
- I would love that let's go to the movies tonight. [Present]
- When has finished the completed one, we can go fishing. [Perfect tense]
- Yes would have paid attention in class, you wouldn't be asking me this. [Imperfect Past]
- Everyone who I would have studied derived, you will understand that class. [Perfect future]
- If i you would have helped, it would have been better. [Past perfect]
- I hope time will accompany so I can go to the park this afternoon. [Present]
- Once you finished the vegetables, I'll serve you dessert. [Perfect tense]
- One who I will request our material, we will send it to you. [Imperfect future]
- My father I would like have everything ready this afternoon. [Imperfect Past]
- If I had known, would have helped. [Past perfect]
- I hope that come out first in the race. [Present]
- Those who would have known The Vatican will pick up the references. [Perfect future]
- When They have passed elections, the economy will be more stable. [Perfect tense]
- I hope not have problems at the airport; They are very demanding. [Present]
- Once we finished to paint, we will buy furniture. [Perfect tense]
- You behave as if were you child. [Imperfect Past]
- It seemed strange to me that would have called throughout the day. [Past perfect]
- One who i will read the rules, he will behave appropriately. [Imperfect future]
- Hopefully for our honeymoon let's do that excursion. [Present]
- Yes had money, I would go on vacation to Morocco. [Imperfect Past]
- I do not want that themes for me, I'll be fine. [Present]
- If not will need help, I wouldn't be asking for it. [Imperfect Past]
- Let me know when beechfinished to order. [Perfect tense]
- Who there isorder additional information, you will receive it in your email. [Perfect future]
- Yes will you help with the preparations, it would be easier for everyone. [Imperfect Past]
It can serve you:
- Sentences with and without verbs
- Conjugated verbs


