Content
The main air pollutants they have been created by man, that is to say they are exogenous pollutants. Gases and other toxic substances are emitted by various human economic activities.
Pollution occurs when the presence or accumulation of a substance negatively affects the ecosystem.
Sources of contamination can take several forms:
- Fixed: They are those that do not change place, this has the effect of accumulating the same harmful substances in a place. The difference in the case of air pollution is that although the source is fixed, the wind can spread the pollutant over a very large area.
- Mobile phones: Those that change places while emitting pollutants, extending the affected area.
- Area: When a large sector has diverse and small sources of pollution that, by the sum of their emissions, affect a considerable area.
- Natural phenomena: The ecosystem can be adversely affected by sources that do not depend on human action. In these cases we speak of endogenous contamination. In the case of air, an example of endogenous pollution is the Volcanic eruptions. However, natural pollutants are not the main air pollutants, as the list will show.
See also: 12 Examples of Pollution in the City
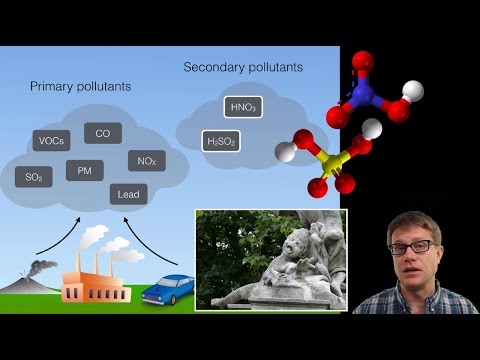
Main air pollutants
Carbon monoxide (CO): Colorless gas highly toxic in high concentrations or by prolonged exposure. It is generally not found in concentrations high enough to cause rapid poisoning. However, stoves that burn fuel (wood, gas, coal) are very dangerous if they do not have an adequate installation that allows an air outlet. Four million people die annually from carbon monoxide poisoning. Comes from
- 86% of carbon monoxide emissions come from transportation (area pollutant in cities and mobile in long-distance transportation)
- 6% fuel burn in industry (fixed pollutant)
- 3% other industrial processes
- 4% burning and other unidentified processes (eg stoves, area pollutants)
Nitrogen oxides (NO, NO2, NOx): Mixture of nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide. Although it is produced in large quantities by human activity, it is oxidized (dissolved by oxygen) in the atmosphere. One of the negative effects of these oxides is that they intervene in the formation of acid rain, becoming pollutants not only of the air but also of the soil and of the water. Comes from:
- 62% of the transport. The concentration of NO2 (nitrogen dioxide) is found in areas close to traffic routes, and negative effects have been found on the respiratory system, even when exposure to this oxide is for short periods.
- 30% of combustion for power generation. Many industries and populations use fuels to generate energy. However, there are cleaner options such as wind, solar or hydroelectric energy that avoids the emission of pollutants.
- 7% is produced altogether by: during the decomposition produced by the bacteria, forest fires, volcanic activity. Much of forest fires are caused by human activity. In addition, bacterial decomposition occurs to a large extent in landfills, due to the degradation of organic waste. In other words, only a small part of the emissions of nitrogen oxides are produced by natural pollutants.
Sulfur dioxide (SO2): A relationship between respiratory conditions in humans and the concentration of sulfur dioxide in the air has been discovered. In addition, it is the main cause of acid rain, which affects the ecosystem as a whole, polluting soils and water surfaces. It comes almost exclusively (93%) from burning fossil fuels (Petroleum derivatives). This burning occurs mainly to obtain energy, but also in industrial processes (“chimney industries”) and in transportation.
Suspended particles: Also called particulate matter, they are the particles solid or liquid that remain suspended in the air. For a non-gaseous substance to be suspended in air, it must have a specific diameter called "aerodynamic diameter" (the diameter that a sphere that has a density of 1 gram per cubic centimeter so that its terminal velocity in air is the same as that of the particle in question). Comes from
- Incomplete combustion of any substance: fossil fuels, waste and even cigarettes.
- They are also silica particles from rock pulverization and from glass and brick making processes.
- Textile industries produce organic dust.
Chlorofluorocarbon (CFC): They were very common in the manufacture of aerosols, although now their use has decreased due to their drastic negative effects on the environment. They are also used in refrigeration systems. This gas binds to the ozone particles of the layer that protects the planet, decomposing it. The call "ozone hole”Leaves areas of the earth's surface defenseless against solar rays that are harmful to humans, plants and animals.
More information?
- Examples of Air Pollution
- Examples of Water Pollution
- Examples of Soil Contamination
- Examples of Pollution in the City
- Main Water Contaminants
- Examples of Natural Disasters


